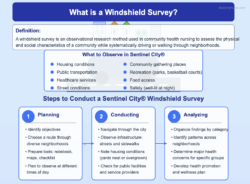
When it comes to improving the well-being of a community, understanding its specific health needs and challenges is absolutely paramount. That’s where a Community Health Needs Assessment, or CHNA, comes into play. It’s a systematic process that helps public health organizations, hospitals, and community groups identify key health issues and develop strategies to address them effectively. A well-designed survey is often the cornerstone of this assessment, gathering direct insights from the very people affected.
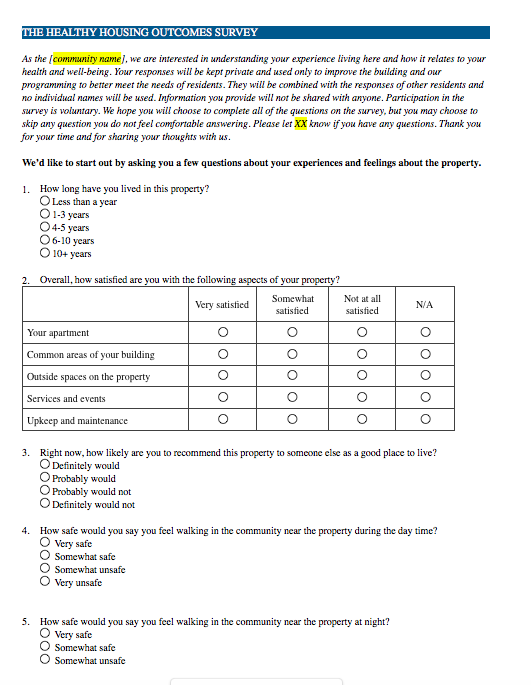
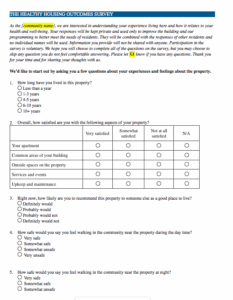
Building a comprehensive survey from scratch can be a daunting task, requiring a lot of thought about question types, phrasing, and data collection. That’s why having a robust community health needs assessment survey template can be incredibly helpful. It provides a structured starting point, ensuring you cover all essential areas and collect actionable data efficiently, saving you time and effort while guaranteeing a thorough understanding of your community’s unique health landscape.
Crafting Your Community Health Needs Assessment Survey: Key Components
Developing an effective survey for a Community Health Needs Assessment involves more than just listing questions. It requires a thoughtful approach to ensure you capture a holistic picture of the community’s health. Your survey should be designed to uncover prevalent health conditions, understand health behaviors, identify barriers to care, and recognize existing strengths and resources within the community. A great community health needs assessment survey template considers all these facets, guiding you through the critical areas to explore.
Demographic Insights
Starting with demographics is crucial because it helps you understand who is responding to your survey and allows you to analyze health disparities across different groups within your community. This data provides context for all other responses, enabling you to identify specific populations that might be disproportionately affected by certain health issues. It’s about more than just numbers; it’s about ensuring your interventions are targeted and equitable.
- Age range (e.g., 18-24, 25-34, 35-44, etc.)
- Gender identity
- Race/Ethnicity
- Household income level
- Education level
- Geographic location or neighborhood
Understanding Health Behaviors and Status
This section dives into the actual health conditions and lifestyle choices of community members. It aims to gauge the prevalence of chronic diseases, assess general health perceptions, and understand common health behaviors that contribute to or detract from overall well-being. The questions here should be clear and non-judgmental to encourage honest responses.
- Self-reported general health status (e.g., excellent, good, fair, poor)
- Presence of chronic conditions (e.g., diabetes, heart disease, asthma)
- Smoking status
- Alcohol consumption habits
- Physical activity levels
- Dietary habits
Assessing Healthcare Access and Gaps
One of the primary goals of a CHNA is to identify barriers that prevent community members from accessing necessary healthcare services. This part of the survey explores people’s experiences with healthcare providers, insurance coverage, transportation to appointments, and the availability of specialized services. Understanding these gaps is vital for developing solutions that improve access for everyone.
- Type of health insurance coverage (if any)
- Ability to access primary care physicians
- Experiences with emergency room visits for non-emergencies
- Availability of mental health services
- Transportation challenges to medical appointments
- Affordability of prescriptions or medical care
Identifying Community Strengths and Resources
It’s not just about identifying problems; it’s also about recognizing what’s working well. This section focuses on existing community assets, such as local parks, support groups, healthy food initiatives, or educational programs. Leveraging these strengths can be just as important as addressing needs, as they often provide a foundation for new health improvement strategies.
- Awareness of local health programs or services
- Participation in community health events
- Access to healthy food options (e.g., farmers markets, grocery stores)
- Availability of safe places for physical activity
- Perception of community support networks
Maximizing Impact: Best Practices for CHNA Survey Implementation
Once you have your comprehensive survey designed, the next crucial step is ensuring it reaches your target audience effectively and that the data collected is reliable and actionable. The implementation phase is just as important as the design, as even the best questions won’t yield useful insights if they aren’t distributed and managed properly. This involves careful planning, ethical considerations, and a robust approach to data analysis.
First, consider your outreach strategy. Who needs to be heard? To ensure a truly representative understanding of your community’s health needs, you’ll want to reach a diverse range of voices. This often means utilizing multiple distribution channels. Think about online platforms for broader reach, but don’t forget about traditional methods like paper surveys distributed at community centers, libraries, or health clinics, especially for populations with limited internet access. Engaging local leaders and trusted community organizations can also significantly boost participation rates and build trust.
Next, prioritize participant privacy and data security. People are more likely to share honest information if they feel their responses are confidential and anonymous. Clearly state your privacy policy and how the data will be used. Ensure your data collection methods, whether digital or physical, are secure and compliant with relevant regulations. Providing options for completing the survey in multiple languages can also vastly improve inclusivity and response quality, making sure everyone feels comfortable sharing their experiences.
Once the data starts flowing in, the real work of analysis begins. This isn’t just about tallying numbers; it’s about identifying patterns, correlations, and key themes. Look for significant disparities across different demographic groups and highlight the most pressing issues identified by the community. Qualitative data, gathered through open-ended questions, can provide rich narratives that add depth to your quantitative findings. Tools for statistical analysis can help validate your observations and uncover hidden insights, transforming raw data into meaningful intelligence.
Finally, remember that the survey is just one part of the CHNA process. The insights gained must then be translated into a clear, actionable plan. Present your findings to community stakeholders in an accessible format, fostering discussion and collaboration. Use the data to prioritize health issues, allocate resources effectively, and develop targeted interventions. The ultimate goal is to empower the community to build a healthier future, making data-driven decisions that genuinely improve lives based on their expressed needs.
Understanding and addressing the health priorities of a community is a dynamic and ongoing process. A thorough Community Health Needs Assessment, powered by a thoughtfully constructed survey, provides the foundational data necessary to make informed decisions and allocate resources effectively. It’s about giving a voice to the community and using their input to drive meaningful, positive change.
By systematically gathering information on health status, access to care, and community resources, organizations can develop targeted interventions that genuinely meet the needs of residents. This collaborative, data-driven approach not only identifies challenges but also highlights existing strengths, paving the way for sustainable health improvements that truly reflect the aspirations and realities of the people they serve.