Ever been in that whirlwind of an emergency department (ED) shift, juggling multiple patients, and needing to document a hand exam quickly and accurately? You’re not alone. The hand, with its intricate anatomy and complex function, can present a diagnostic challenge. And when time is of the essence, having a structured approach to documentation is crucial. That’s where a hand exam documentation template for emergency medicine can be a lifesaver.
Think about it: a patient comes in with a suspected fracture, a laceration, or maybe just unexplained pain. You need to rapidly assess their condition, rule out serious injuries, and initiate appropriate treatment. But doing so efficiently requires a systematic examination and a clear record of your findings. A well-designed template guides you through the essential components of the hand exam, ensuring nothing gets missed even in the high-pressure environment of the ED.
This article will delve into the key elements of hand exam documentation in emergency medicine. We’ll explore what to include in your notes, why it’s important, and how a template can streamline the process, improving both patient care and your own workflow. We’ll also give you some tips on how to use a hand exam documentation template emergency medicine effectively.
Why a Structured Hand Exam is Essential in Emergency Medicine
In the fast-paced environment of the emergency department, it’s easy to fall into the trap of hurried assessments. However, a structured hand exam is not a luxury; it’s a necessity. The hand’s complex anatomy, comprising bones, ligaments, tendons, nerves, and blood vessels, demands a systematic approach to ensure accurate diagnosis and management. Imagine missing a subtle tendon injury or a developing compartment syndrome – the consequences could be devastating for the patient’s long-term function.
Clear and comprehensive documentation serves several crucial purposes. First, it provides a detailed record of the patient’s initial presentation, which is essential for tracking progress and making informed treatment decisions. Second, it facilitates communication among healthcare providers. If a patient is transferred to a specialist or requires follow-up care, a well-documented hand exam provides the receiving team with a clear understanding of the patient’s condition and the initial findings. Finally, accurate documentation is crucial for medico-legal reasons. In the event of a lawsuit, a detailed and objective record of the hand exam can be invaluable in demonstrating the standard of care provided.
A structured approach, facilitated by a documentation template, minimizes the risk of overlooking important details. It prompts you to assess each aspect of the hand in a systematic manner, from observation and palpation to range of motion and neurological function. This reduces cognitive load, particularly in stressful situations, and allows you to focus on the patient’s specific complaints and concerns.
Moreover, standardization improves consistency. When all providers use the same template, the quality and completeness of the documentation become more uniform. This makes it easier to compare findings over time and to identify subtle changes that might indicate a worsening condition. Standardized documentation also facilitates research and quality improvement initiatives.
Ultimately, a structured hand exam, guided by a comprehensive documentation template, benefits both the patient and the healthcare provider. It ensures a thorough assessment, facilitates communication, minimizes the risk of errors, and promotes high-quality care in the demanding setting of the emergency department. The use of a hand exam documentation template emergency medicine is highly recommended to improve patient care.
Key Components of a Hand Exam Documentation Template
A comprehensive hand exam documentation template should include several key components to ensure a thorough and accurate assessment. These components can be broadly categorized as follows: Subjective Data, Objective Data, Assessment, and Plan (SOAP).
The Subjective Data section captures the patient’s history and symptoms. This includes the chief complaint (the reason for the visit), the mechanism of injury (if applicable), the onset and duration of symptoms, any previous hand injuries or surgeries, and relevant medical conditions. It’s important to document the patient’s description of pain, including its location, intensity, and character (e.g., sharp, throbbing, burning). Also, document any associated symptoms, such as numbness, tingling, or weakness.
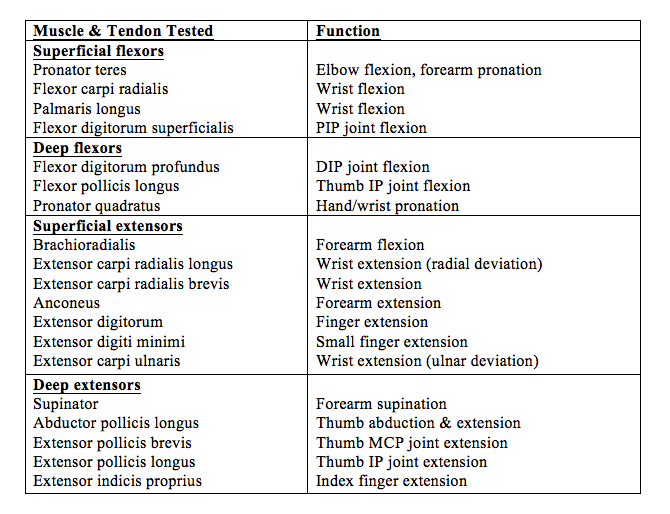
The Objective Data section documents the physical examination findings. This includes a detailed description of the appearance of the hand, including any swelling, bruising, deformities, or open wounds. Palpation should be performed to assess for tenderness, crepitus, and masses. Range of motion should be assessed at each joint, including the wrist, fingers, and thumb. Neurological examination should include assessment of sensation (light touch, two-point discrimination) and motor function (strength testing of individual muscles). Vascular assessment should include palpation of the radial and ulnar pulses, as well as assessment of capillary refill. Special tests, such as the Finkelstein test (for De Quervain’s tenosynovitis) and the Tinel’s test (for carpal tunnel syndrome), should be performed as indicated.
The Assessment section summarizes the findings and provides a differential diagnosis. Based on the subjective and objective data, you should list the most likely diagnoses and consider other possible conditions that could explain the patient’s symptoms. The Plan section outlines the next steps in management, including any further investigations (e.g., X-rays, CT scans, MRI), treatment options (e.g., immobilization, pain medication, surgery), and follow-up instructions.
Finally, remember to include any pertinent negatives. Documenting what you specifically ruled out is just as important as documenting what you found. For example, if you specifically tested for and ruled out a scaphoid fracture, document this finding. A well-structured hand exam documentation template for emergency medicine should prompt you to consider and document all relevant aspects of the examination.
Documenting the hand exam in emergency medicine is important and helps with the overall treatment plan of the patient.
It’s important to be thorough, clear, and objective in your documentation. Avoid vague terms like “normal” or “unremarkable.” Instead, describe your findings in detail. For example, instead of saying “range of motion is normal,” specify the degrees of flexion and extension at each joint. Using a standardized template ensures consistency and reduces the risk of overlooking important details.
Accurate and thorough documentation is the bedrock of quality medical care. By adopting a systematic approach and utilizing a well-designed template, you can ensure that your hand exams are comprehensive, consistent, and defensible. This ultimately leads to better patient outcomes and reduces the risk of errors and complications.
Remember that utilizing and continuously improving the hand exam documentation template emergency medicine, will improve clinical workflows.